The Dynamic REd All-sky Monitoring Survey is a near-infrared fully automated all-sky survey that will be conducted using a custom built 0.5m telescope that will be located at the Australian National University’s Siding Spring Observatory.

DREAMS is designed to search for astronomical transient and variable events every night. An example of these types of events is a an exploding star known as a supernova. The video below shows SN 2018gv as captured by the Hubble space telescope.
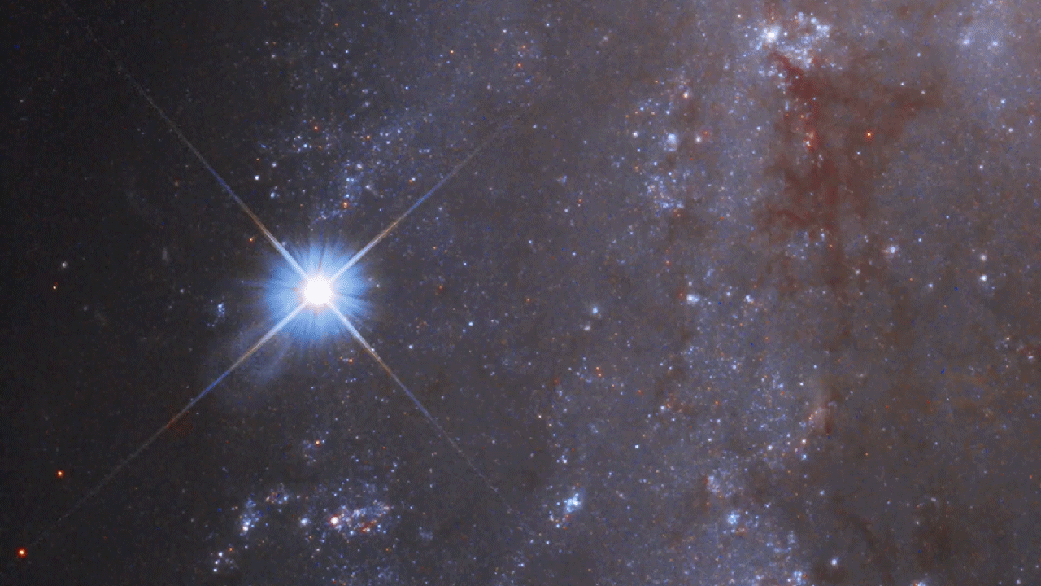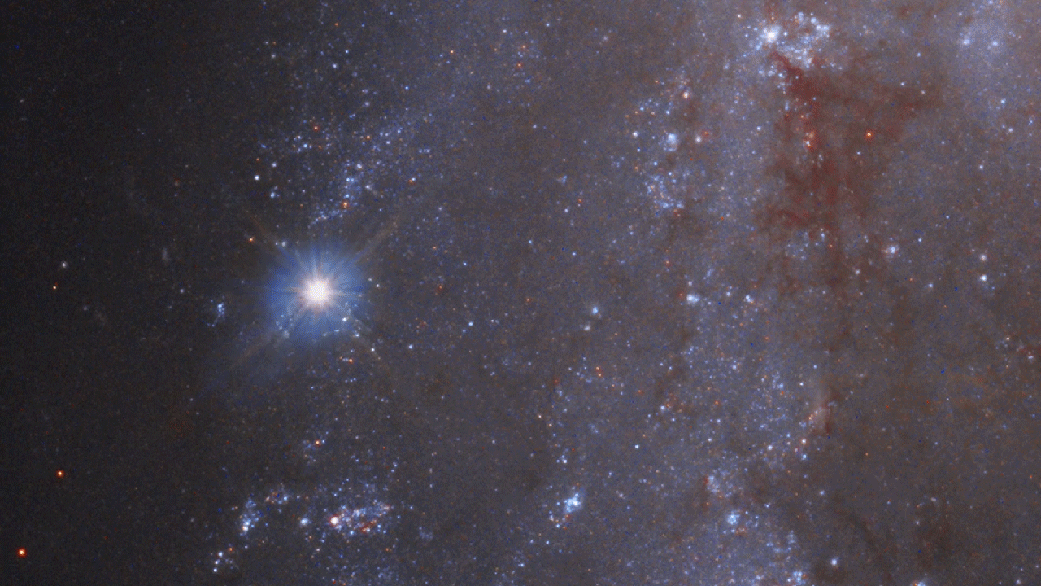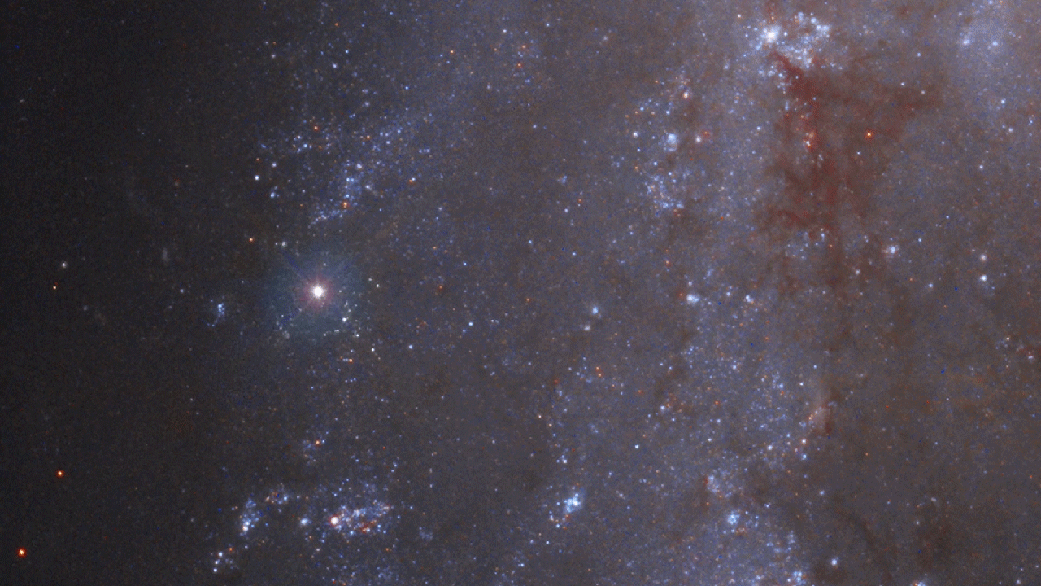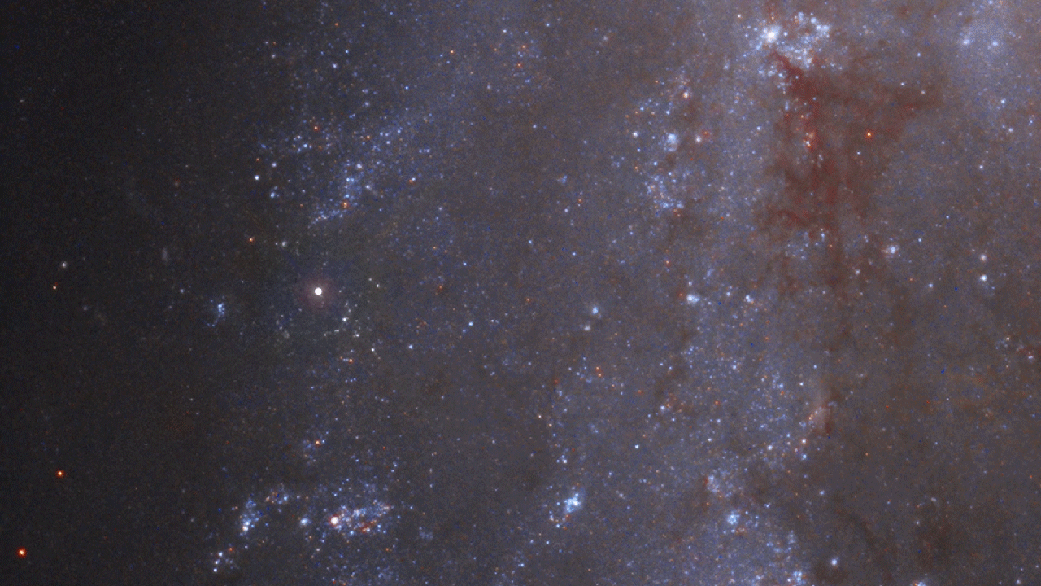
Credit: NASA, ESA, J. DePasquale (STScI), M. Kornmesser and M. Zamani (ESA/Hubble), A. Riess (STScI/JHU) and the SH0ES team, and the Digitized Sky Survey
DREAMS will create reference images of the southern sky and then use a data reduction and analysis technique known as difference imaging to detect these type of events and more.
DREAMS consists of two major components, the optical tube/telescope assembly (OTA) and the imager/instrument. The table below lists the major properties for each component, the final survey specifications are primarily determined by the instrument properties.
| DREAMS | OTA | Instrument |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | 0.5m | |
| F/ratio | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| Field of View | 12.19 square degrees | 3.71 square degrees |
| Pixel scale | 2.48"/pixel | |
| Operating Wavelengths | 0.9 - 1.7 µm | |
| Filters | (Y), J, and H | |
| Survey Depth | 17.8 MAB | |
| Survey Speed | Visible sky every 4 nights |
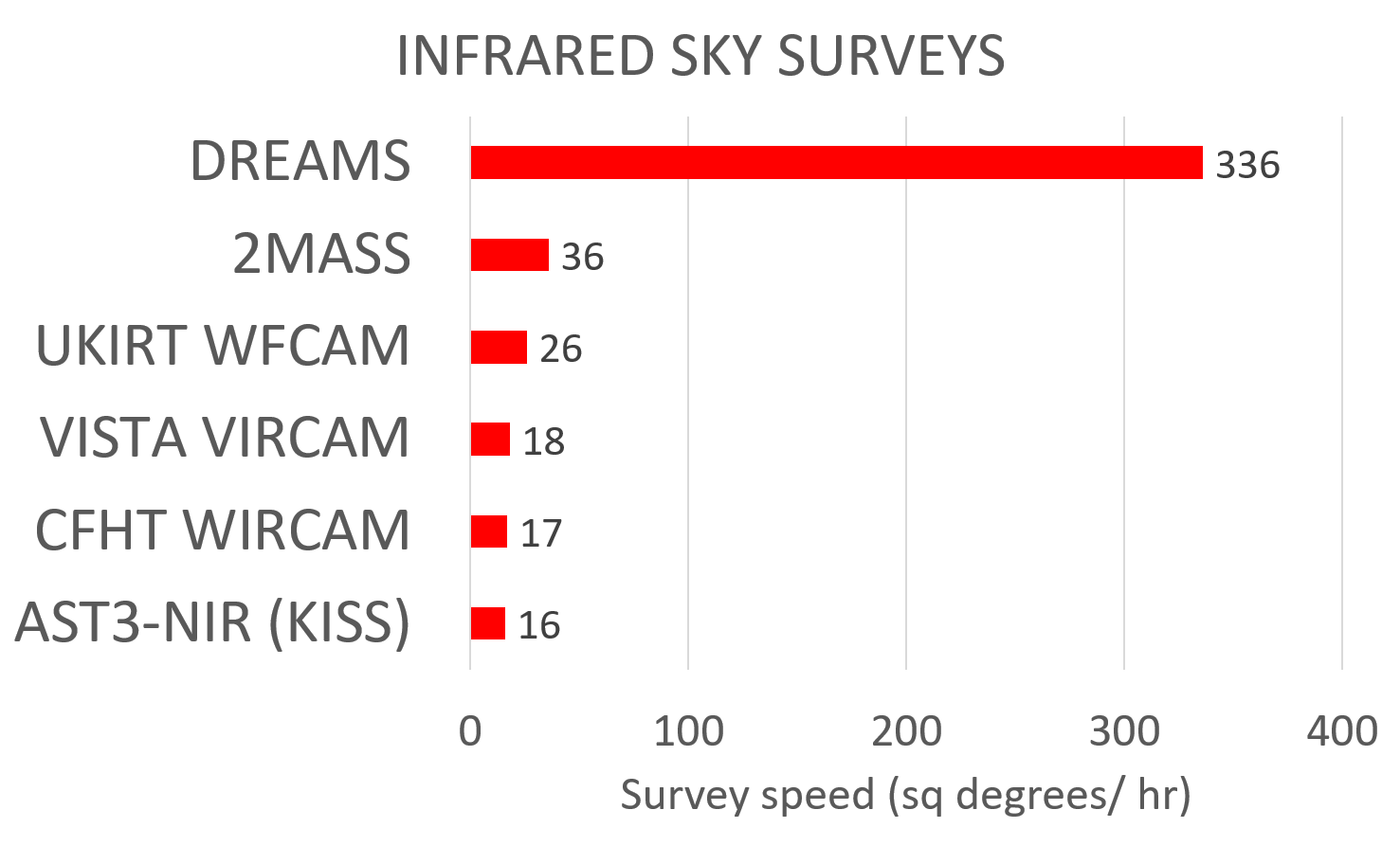
The large field of view of DREAMS will allow it to fulfill a unique part in near-infrared astronomical surveys. The following comparison compares the survey speed at the DREAMS magnitude limit against other previous surveys.
Recent Updates
-
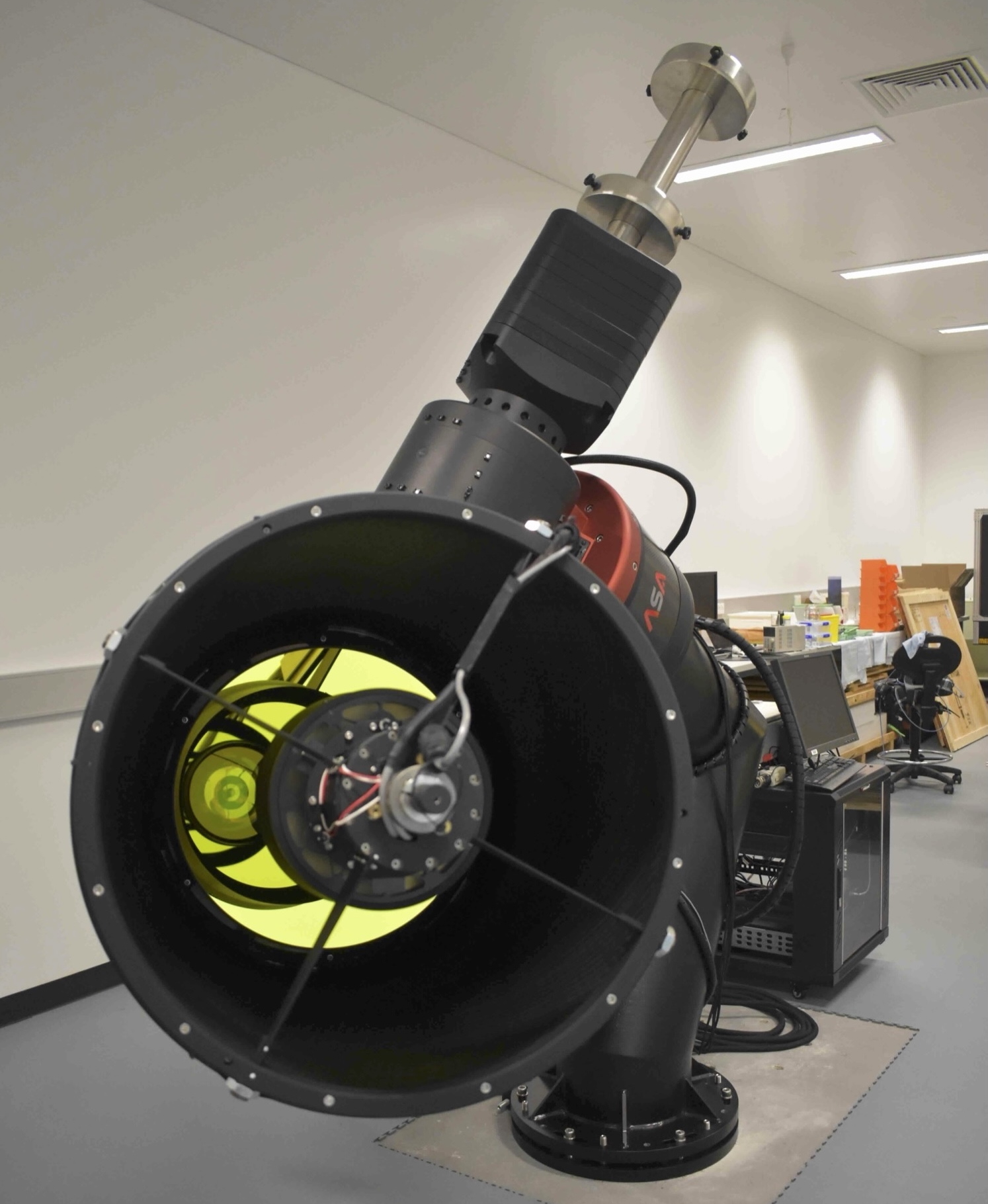
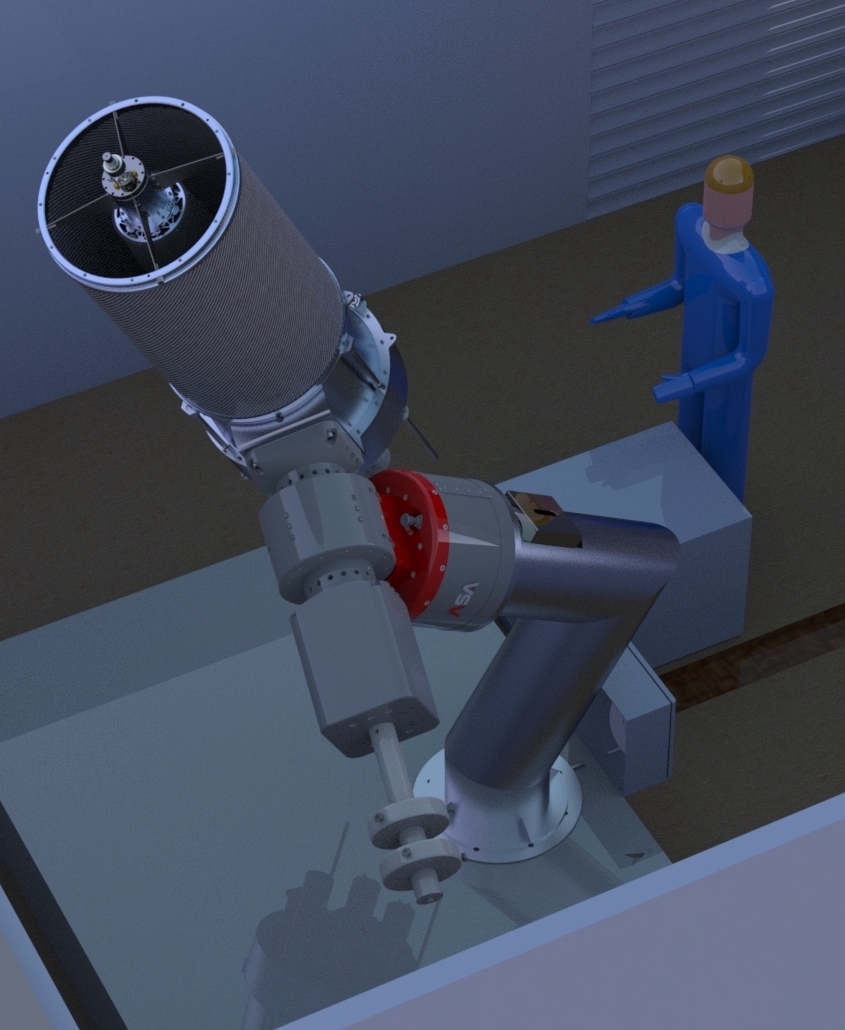
Majority of assembly completed
The majority of the assembly and alignment of DREAMS has been completed. The following image shows the telescope within the laboratory at Mt. Stromlo Observatory.